Google Chrome is without a doubt one of the most popular web browsers available today, thanks to its simplicity, reliability, and ecosystem of browser extensions. However, due to its high resource demands, users who are running low on system resources, such as RAM or CPU, may find it challenging to keep the browser running smoothly. To address this issue, Chrome comes with a feature called “Memory saver,” which can help save system resources by suspending tabs that are not in use.
While this feature can be a boon to some users, it is a curse for others: Take, for example, Graphic Designers or Product Designers who switch frequently between Shutterstock, icons8, and Figma. To summarize this scenario, the Chrome Memory Saver feature will slow down your workflow and spike CPU resource usage if you frequently switch between multiple tabs or need to access certain previously opened websites very often and quickly. This is because the page would need to be reloaded after being idle for, say 5 minutes.
How Chrome’s Memory Saver Works
The Chrome browser memory saver feature works by identifying tabs that have been inactive for a specific period, typically five minutes. Once a tab is deemed inactive, the browser suspends it, freeing up system resources that would have been used to keep the tab running in the background. When a user clicks on the suspended tab, the page is automatically reloaded and the user can continue from where they left off. This process is designed to help users save system resources and keep the browser running smoothly, especially on devices with limited RAM or CPU.
The Drawbacks of Enabling Memory Saver on Chrome
The downside of the memory saver feature is that it can slow down your workflow, especially if you frequently switch between tabs or use certain websites regularly. For instance, if you are working on a research project and need to refer to multiple web pages simultaneously, the memory saver feature may suspend some of your tabs, making it difficult to access the information you need quickly. You may have to wait for a few seconds for the tab to reload, which can be frustrating and time-consuming, especially if you are working on a tight deadline.
Moreover, the memory saver feature can also interfere with certain web applications, such as online banking, user registration, survey websites, or shopping websites. These types of sites often require constant updates and real-time data transmission to stay alive, and suspending them can cause errors or glitches in the application. This can result in frustration for the user and may even lead to data loss or financial losses in the case of online banking.
Subscribe for updates
Luckily, you can create exceptions by “whitelisting” some websites from inside Chrome’s performance settings, or you can disable Chrome’s memory saver feature altogether.
How To Disable Chrome’s Memory Saver
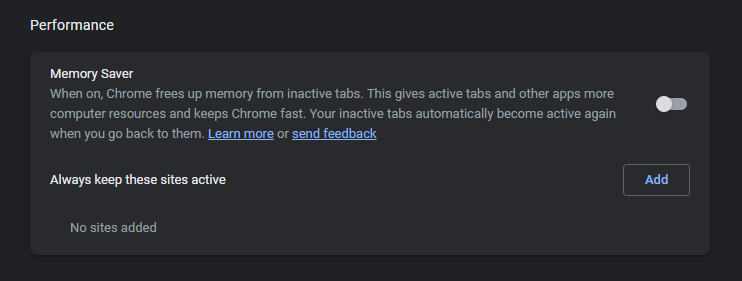
Memory Saver toggle screen
Chrome’s Memory Saver is often enabled by default in recent versions of the browser. However, if you have made up your mind to disable this feature, you can follow these steps:
- Open Chrome on your computer.
- Click on the three dots icon in the top-right corner of the browser window.
- Select “Settings” from the drop-down menu.
- Look at the pane on your left, and click on “Performance“.
- Use the switch to toggle the Memory Saver feature.
You can also add a list of sites to be kept active even though memory saver is left enabled. The choice is all yours.
Note that disabling the Memory Saver feature may cause Chrome to use more system resources and may slow down your browser’s performance. If you have a device with very limited RAM or CPU, and switch tabs less frequently, it is better to keep the feature enabled.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while Chrome’s memory saver feature can be a helpful tool for users who are struggling with limited system resources, it can also slow down your workflow, especially if you frequently switch between tabs or use multiple websites regularly. If you find yourself missing deadlines often, it’s time to look towards the memory saver feature, you may consider disabling it. Ultimately, it is really up to you to decide whether the memory saver feature is a helpful tool or a hindrance to your workflow.